How does sand casting support rapid prototyping projects? And just how fast is the process?
Prototyping decreases development time within a project by allowing design optimisation and modification. This can help reduce development time, as well as the risk of any costly mistakes and engineering changes. Performance and life span of the product can also be increased by optimisation across design and manufacturing process.
Why prototype with sand casting?
Sand casting is a highly technical, complex manufacturing process. Prototyping with sand casting gives engineers huge flexibility when compared to many other prototyping methods.
- Sand casting is a flexible process, allowing for design modifications throughout the process (making it ideal for prototyping to test function, form or concept)
- Sand casting is a fast process, creating prototypes in a number of weeks
- Prototypes created using sand casting are often much more cost effective than other production method.
- Sand casting can create complex geometric shapes in a single net part, ideal for innovative approaches to lightweighting and part count reduction.
- A range of alloys can be used in sand casting
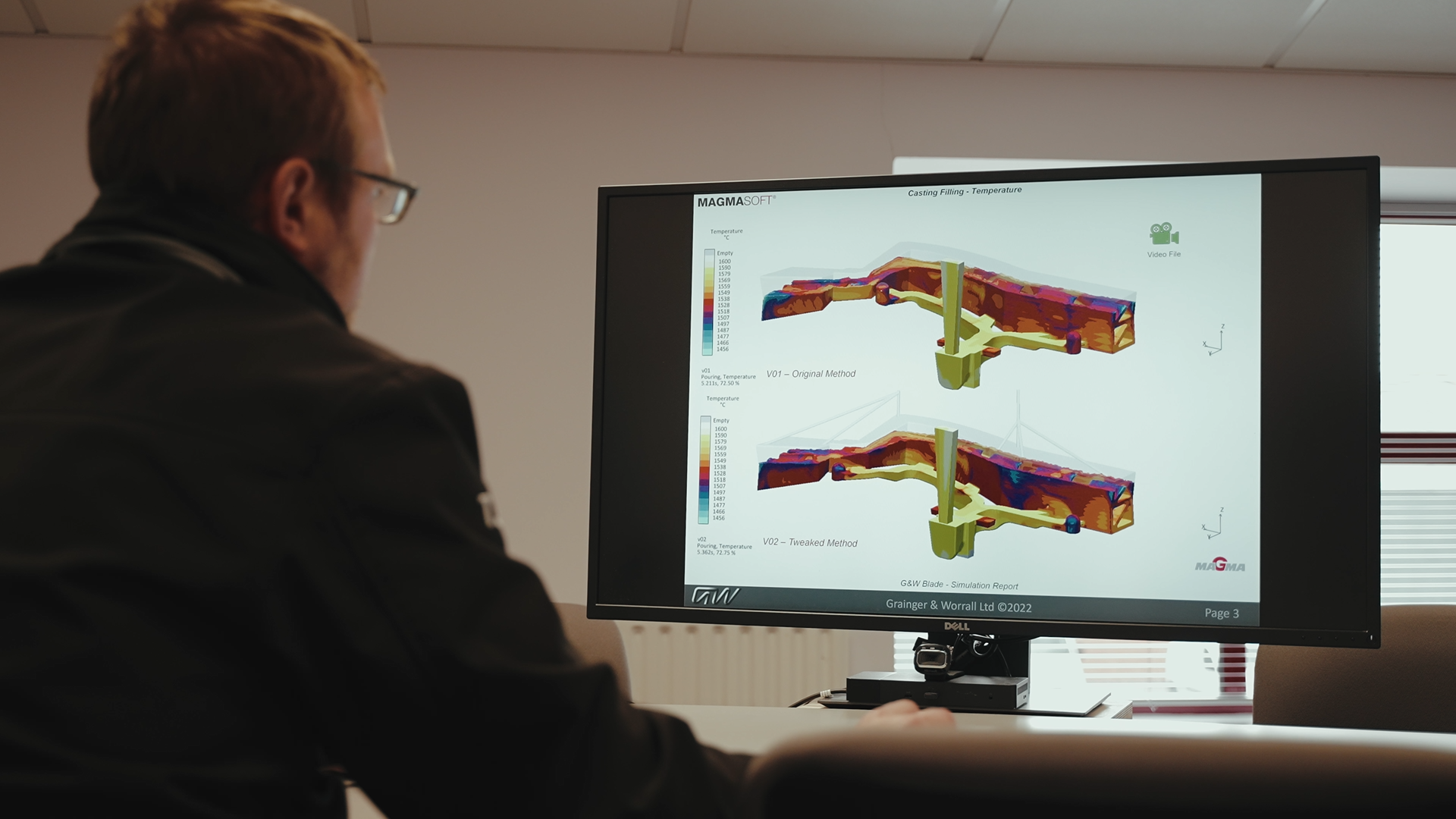
- Modern sand casting is a data-driven, highly technical process involving multiple technologies
The flexibility of sand casting means there are multiple opportunities throughout the process to influence part characteristics, making it particularly suitable to modification and optimisation needed in prototyping.
What is the difference between Rapid Production and Make Like Production (MLP)?
Sand casting can support both Rapid Prototyping and Make Like Production (MLP) processes.
Rapid prototyping is used where development and lead times are critical, and utilises simulation, engineering, tooling, casting, machining and validation. Rapid prototyping has a quicker turn around than MLP processes, typically approximately 8 weeks.
In rapid prototyping, a frozen design is provided by the customer.
Make Like Production (MLP) is used where prototypes need to mimic production quality. Typically, an additional 4 weeks of design time is added to standard rapid prototyping lead time. MLP with sand casting creates solutions for specifications on material property tolerances, alloy compositions and dimensional accuracy

Want to know more about sand casting and prototyping?

We’ve written a guide on The Basics of the Sand Casting Process. Full of GW insights, it’s a quick primer on how to design, make and test complex metal shapes in prototyping.
We’ve also included some useful questions you can ask your casting supplier, ensuring you’ll achieve the best quality casting for your next project. These include:
- How do you design, make and test a quality casting?
- What are the benefits of sand casting in prototyping?
- What are the applications sand casting is (and isn’t) suitable for?
To get your free copy of The Basics of the Sand Casting Process, click on the button below.

 Get in touch
Get in touch


